Which Shows the General Structure of an Ether Apex
Summary of APEX1 APE APE-1 APEN APEX APX HAP1 REF-1 REF1 expression in human tissue. Other workers have shown that a Cr 3 complex ha s a distorted octahe dral.

Crystal Structure Of Ethyl 2 Methyl 4 5 Methylthiophen 2 Yl 5 Oxo 1 4 5 6 7 8 Hexahydroquinoline 3 Carboxylate C18h21no3s
They carry instructions for making proteins.

. The Composition and Structure of Ether. Figure Figure4B 4 B shows a near-median longitudinal section of a rice vegetative shoot apex at a higher magnification than Figure Figure4A. Closely related to alcohol -- both through history and chemistry -- is ether ethyl ether diethyl ether a compound obtained from alcohol by the action of oil of vitriol sulfuric acid.
A reaction that involves unsaturated monomers often alkenes reacting with one another to form polymeric chains that are saturated. Have two groups attached to show cis-trans isomerism. The double bonded structure is regarded as the major contributor the middle structure a minor contributor and the right hand structure a non-contributor.
What is the common name of the ether that has the following structure H3C-O-CH2-CH3 Using the reagents below list in order by letter no period those necessary to prepare diethyl ether from ethane. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is RCOOH or RCO2H with R referring to the alkyl alkenyl aryl or other group. Figure 3 shows a representative MSMS spectra of PEP-1802045Z8Z11Z14Z an ether-linked phosphatidylethanolamine PE in one of our samples that was identified in negative mode and a previously published spectra of the same ion confirming our tentative identification of that ion.
We are asked to compare. Ketones and aldehydes both contain carbonyl groups. Signifies that both R groups need not be the samedimethyl ether CH3OCH3Ethyl methyl ether CH3OC2H5.
They speed up chemical reactions. Question 9 9a Which describes the molecule below. Lines 1 2 and 3 indicate approximate planes of the cross-sections shown in Figure Figure4 4 E F and G respectively.
Structural formulas of ethers esters and carboxylic acids R and R are alkyl or aryl group. A carbonyl group consists of a carbon atom with a double bond to an oxygen atom. If the carbonyl group is on the end of the molecule with a hydrogen atom on.
They store genetic information. A general observation that the more bonding electrons in a given bond the shorter and stronger the bond. Reference to Table 1 shows that within the meris-tem as a whole structure can be separated from func-tion.
This structure has 5 chiral carbons C and no special symmetry elements it has no planes axes or centers of symmetry so it has the 32 different stereoisomers shown in Figure 2005 next page. Draw the structure for each compound. Up to 10 cash back In general the outer form of the cochlea had a cylindrical structure in parallel with the size of the animal the width and height of the cochlea had expanded considerably.
What is the general function of enzymes in the human body. Recently we developed a new technique for the analysis of intact core tetraether lipids in cell material and. Isoprenoid glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers GDGTs and branched glycerol dialkyl diethers are main membrane constituents of cultured hyperthermophilic archaea and eubacteria respectively and are found in environments with temperatures 60C.
If a carbonyl group is between two carbons it forms a ketone. The preparation of alcohol spirit of wine vinic alcohol ethanol ethyl alcohol by fermentation dates to antiquity. This is likely due to the difference in structure.
What is a colorless flammable sweet-smelling liquid that was once used in surgeries as anesthesia. The general pyranose structure for glucose is also the general structure of many other monosaccarides Figure 2004 above. Seen in figure 311a which shows the X-ray structure of one of the isomers of a Co 3 complex 39.
The boiling and melting point of ethanol is higher than dimethyl ether. It was observed that the cochlea localized around the modiolus turned in 35 turns basal media and apex and the apex part is in the form of a dome. The lengths of single C-C bonds also vary significantly depending on what other atoms or groups are attached to the car- bons.
H 3 C - O - CH 3. What shows the general structure of an ether. For ethanol the structure is.
They make fatty acids unsaturated. A carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group COOH attached to an R-group. It is supposed that roots of contemporary species within taxonomie divisions which are in evolutionary terms in advance of the Lycopsida possess a number.
Since the middle charge-separated contributor has an electron deficient carbon atom this explains the tendency of electron donors nucleophiles to bond at this site. The carbonyl group is -CO. Its B for the fellow failures in apex i trusted the picture below and got my average dropped to a 4.
Key Takeaway Alkynes are hydrocarbons with carbon-to-carbon triple bonds and properties much like those of alkenes. Now up your study game with Learn mode. A general reaction involving a reactant adding to an unsaturated bond to form a substituted alkane.
The general formula for an ether is R-O-R where R. Although ether is no longer used as a. The cells at the apex and their proliferative properties.
Esters are a class of organic compounds that are derivatives of inorganic or organic acids in which the hydrogen of the hydroxyl group of the carboxylic acid is replaced by a hydrocarbon radical. You just studied 48 terms. The structure of dimethyl ether is.
Carboxylic acids occur widely. Ethanol is able to form hydrogen bonds because of the -OH group on the end. Draw the structure for each compound.
Which shows the general structure of an ether Which term explains whether an objects velocity has increased or decreased over time. The general formula for esters is shown in Fig. H 3 C - CH 2 - OH.
An amino acid with three side chains B.

The Crystal Structure Of Tris 6 Methylpyridin 2 Yl Phosphine Selenide C18h18n3pse

The Synthesis And Crystal Structure Of Ethyl E 1 2 6 Dichloro 4 Trifluoromethyl Phenyl 5 2 Methoxybenzylidene Amino 4 Trifluoromethyl Sulfinyl 1h Pyrazole 3 Carboxylate C22h15n3cl2f6o4s

The Crystal Structure Of Tris 4 Methyl 1h Pyrazol 1 Yl Methane C13h16n6

The Crystal Structure Of 7 Bromo 2 4 Chloro Phenyl Quinoxaline C14h9brcln2

Human Body System Inside The Human Skull Human Skull Anatomy Skull Anatomy Skull

Crystal Structure Of 6ar 6a1s 10as 2 4a 6a 6a1 9 10 Hexahydro 7h 4 5 Methanocyclobuta 4 5 Naphtho 8a 1 B Pyran C15h16o

Crystal Structure Of Cyclopropane 1 2 3 Triyltris Phenylmethanone C24h18o3

Crystal Structure Of Bis 5 Ethoxy 2 1 Hydroxy 2 Methyl 3 Oxidopropan 2 Yl Imino Methyl Phenolato K3n O O Manganese Iv Methanol 1 1 C27h38mnn2o9

Detailed Sacrum Osteology Osteology Human Anatomy And Physiology Thoracic Vertebrae

Crystal Structure Of E 1 2 Cyano 3 Oxo 1 Phenylprop 1 En 1 Yl 3 7 Diphenylindolizine 6 Carbonitrile C31h19n3o
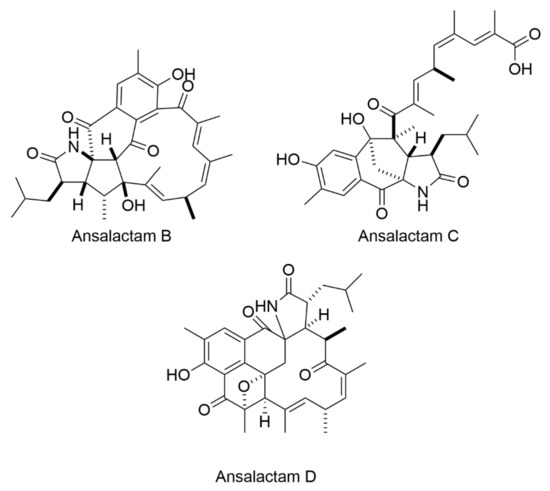
Antibiotics Free Full Text Identification Of Bioactive Compounds From Marine Natural Products And Exploration Of Structure Activity Relationships Sar Html

Crystal Structure Of Poly Bis M2 2 6 Bis 1 Imidazoly Pyridine K2 N N Bis Thiocyanato K1 N Copper Ii Dithiocyanate C24h18cun12s2

Crystal Structure Of 1 1 Methane 1 1 Diyl Bis 3 Methyl 1h Imidazol 3 Ium Bis Hexafluoridophosphate C9h14f12n4p2

Crystal Structure Of N 4 Bromo 2 6 Dichloro Phenyl Pyrazin 2 Amine C10h6brcl2n3

Crystal Structure Of 1 4 Chloro Phenyl 7 Ethoxyl 6 8 Difluoro 4 Oxo 1 4 Dihydro Quinoline 3 Carboxylic Acid C18h12clf2no4

Crystal Structure Of Ethyl 1 4 Fluorophenyl 4 Phenyl 1h Pyrrole 3 Carboxylate C19h16fno2
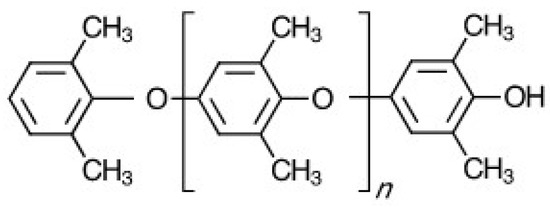
Polymers Free Full Text Poly Phenylene Ether Based Amphiphilic Block Copolymers Html

The Crystal Structure Of Dichlorido 2 4 Phenyl 2h 1 2 3 Triazol 2 Yl Methyl Pyridine K2n N Palladium Ii C14h12cl2n4pd

Comments
Post a Comment